Hyperhidrosis (Sweat Reduction) Treatment
regular: $1,190
new customers special: $1,011
(price for 100 units)
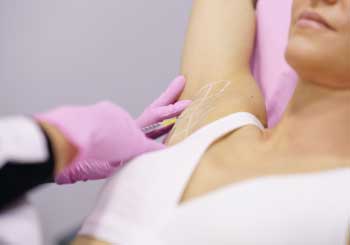
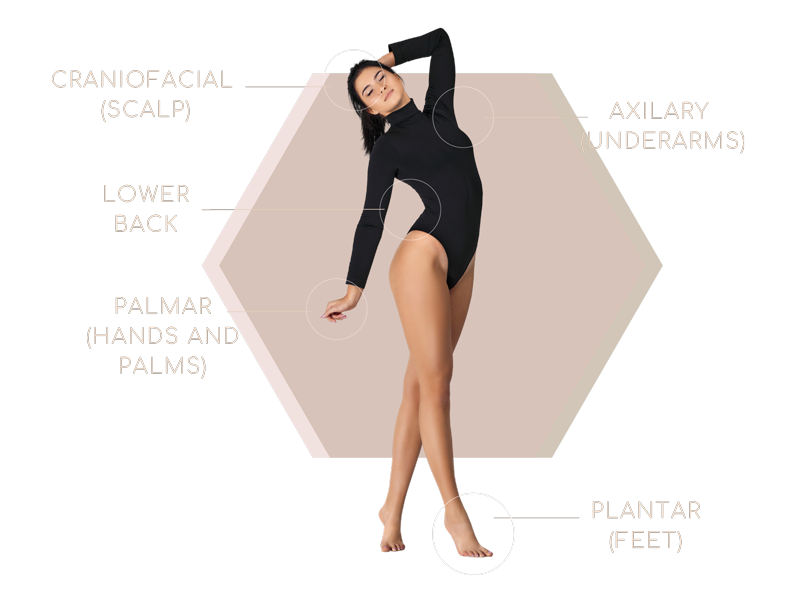
You can treat excessive sweating in the areas of your body that are prone to Hyperhidrosis, such as the armpits, hands, scalp, or feet.
 Stop Underarm Sweating
Stop Underarm Sweating
Prevent Sweaty Feet
 Treat Palmar Hyperhydrosis
Treat Palmar Hyperhydrosis
 Extend your Blowouts with Scalp Botox
Extend your Blowouts with Scalp Botox
New to StudioMD?
Enjoy 15% off with code NEWGLOW
Become a Member
Enjoy 20% off with code MEMBER20
Not a member? No problem! Purchase the offer now and sign up for a membership ($99 annual fee) in-store before your treatment.
BUY A PACKAGE NOW
1. Make your purchase below.
2. Receive your automated confirmation email upon purchase.
3. Follow the instruction in the email to reserve your prepaid appointment at your location of choice.
2 Promotions are only valid for advanced online purchases.
HYPERHIDROSIS
Classic Areas of Excessive Sweating
Dr. Talat, Board-Certified
Dr. Afnan Talat, MD, is a board-certified family medicine physician with over 9 years of experience in medical practice. She is an expert in anti-aging and aesthetic medicine, specializing in Botox, fillers, weight loss, and sexual health management. Dr. Talat's has also worked at prestigious skincare brands' labs, such as Estée Lauder and Clinique, where she formulated and tested the best, clean skincare products. Dr. Talat is committed to a holistic approach to patient care.
Dr. Alcarez, DO
Dr. Kathryn Alcarez is a highly experienced Primary Care Physician with a remarkable focus on injectable treatments for over 5 years. With an educational background from Boston University, she has cultivated her expertise in a range of specialized areas, including Fillers, Radiesse, and Sculptra for body and hand rejuvenation. Dr. Alcarez is also extremely-versed in wellness and weight loss treatments. With her holistic approach, Dr. Alcarez strives to provide comprehensive care that addresses both the physical and motional well-being of her patients.
Dr. Malkin, Board-Certified
Dr. Larry Malkin, DO, is a board-certified physician dedicated to providing exceptional patient care with a focus on fostering partnerships with his patients for the best-personalized results. Dr. Malkin is an expert in anti-aging and aesthetic medicine, specializing in Botox, Sculptra, fillers and sexual health management, treating erectile dysfunction and other conditions. Patients trust his expertise because he consistently delivers high-quality care, ensuring positive and lasting health outcomes.
READY TO BOOK A FREE CONSULTATION?
Easy Peasy!
Submit Form Below or Click to Book Online or Call (718) 313-0094
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Botox injections are used to disable the sweat glands. Botox acts by blocking acetyl choline release at the nerve endings that stimulate the sweat glands thus shutting down the sweat process on the injected sites. The effects can last from 6-12 months depending on the site of injections. The procedure when used for underarm sweating has been approved by the FDA, thus giving new hope for people who after failing to respond to topical treatments were compelled to face surgery.*
Our doctors identify the hyperactive sweat area or areas with Minor’s Starch Iodine test and then, 10 to 15 sites, approximately 2 cm apart, are injected into each axilla. The whole procedure may take 20-30 minutes including the Botox preparation.*
50 units of Botox are usually needed for each axilla. The number of units required may vary depending on the individual patient. Visible results are usually seen in just a few days.*
Note: our doctor team uses Preserved Normal Saline for reconstitution of Botox which decreases the discomfort of the injections.
Most people with excessive sweating are bothered primarily when they are emotionally stressed, physically active, or over-heated. Botox® can prevent sweating for months by blocking the release of the neurotransmitter, i.e., acetylcholine, from the nerve endings, that causes the glands to produce sweat.
Aluminum chloride hexahydrate and salts are used in topical antiperspirant sticks, creams, lotions and solutions. These prevent sweating by clogging the sweat ducts in the skin. These products can be irritating with continued use and are largely ineffective in people with excessive sweating.
Anticholinergic drugs and tranquilizers
Oral medications currently used often provide relief but can cause dry mouth and blurry vision. Tranquilizers may minimize one's anxiety, but do little to diminish actual sweating.
Tap Water Iontophoresis
Battery-powered electrical devices that use water, consist of a moist pad and a prickly electrical current held against skin for several hours. Although they decrease sweating in some people, they are time consuming and they need to be repeated on a daily or a weekly basis. Iontophoresis is mildly effective for severe cases.
Surgery - ETS technique
Surgical alternatives include cutting the sweat glands from the skin of the underarms, therein leaving visible scars and permanent numbness of the skin for decreased sweating. Neurosurgeons now use a fiberoptic surgical tube, to cut nerves in the neck which lead to the axillary sweat glands, i.e. endoscopic sympathectomy.
Risk and side effects of ETS procedure:
Infection, bleeding, and damage to the nerves.
Compensatory sweating: When this occurs the body "makes up" for the decreased sweating in the treated area by producing more sweat in other areas of the body. Approximately 85% of patients will experience some degree of compensatory sweating. It is important to note that compensatory sweating does not improve with time and is the main cause of dissatisfaction with the procedure.
Gustatory Sweating: Increased sweating when patients eat.
Horner’s Syndrome: Presents with unilateral decreased facial sweating, drooping of the eyelid, and enlarged pupils.
Pneumothorax: Air or gas can collect in the chest cavity, which may cause the lung to collapse.
For more information on Botox for Hyperhidrosis you may check https://www.botox.com/
*Results can vary based on individual conditions
LOCATIONS & DIRECTIONS



 Book Online
Book Online